中国航空工业集团公司洛阳电光设备研究所, 河南 洛阳 471000
传统HUD显示精度测试固定选取少量测试点, 试验结果无超差时判断合格, 无法证明是否满足总体要求, 因此需对该方案进行改进。采用数理统计中的推断性统计理论, 结合HUD视场特点, 设计一种简单随机抽样模型, 进行抽样测试, 再基于样本试验结果对总体要求进行推断。首先, 采用简单随机抽样理论, 设计了满足均匀分布的随机样本模型; 然后, 采用假设检验理论, 研究出显示精度决策流程, 确定显示精度超差数、最低样本容量和最大允许超差数之间的关系; 最后设计了验证方案, 试验结果证明了改进方案的合理性。该改进方案可同时兼顾生产方和使用方风险。
HUD显示精度 简单随机抽样 均匀分布 假设检验 样本容量 生产方风险 使用方风险 HUD display accuracy simple random sampling uniform distribution hypothesis test sample size producer risk user risk
西安建筑科技大学信息与控制工程学院,陕西 西安 710055
针对现有多目标检测网络对动态火焰特征提取及增强能力不足,检测效果不佳的问题,提出基于动态形状特征提取及增强的改进YOLOv3火焰检测算法。采用小尺寸结构的ResNet50_vd作为YOLOv3的主干网络,减少特征信息冗余;在主干网络stage 4和stage 5中加入可变形卷积模块,控制采样网格随火焰目标形状的动态变化;引入交并比(IoU)Aware模块,增加置信度得分与IoU定位精度的相关性,提高网络的火焰特征提取能力;同时在YOLOv3 Head中加入Drop Block,引入IoU预测分量优化损失函数,提高模型学习过程中的特征增强能力。通过消融实验验证各改进部分对模型的提升效果,实验结果表明,改进模型对火焰的检测精度达94.11%,推理速度达73.52 frame/s,能够有效满足对动态形状火焰的检测要求。
火焰检测 动态形状 ResNet50_vd 卷积神经网络 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(24): 2410003

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
3 School of Electronic, Electrical and Communication Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
5 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518052, China
6 e-mail: ml@semi.ac.cn
In recent years, parity-time (PT) symmetry in optoelectronic systems has been widely studied, due to its potential applications in lasers, sensors, topological networks, and other fields. In this paper, a time-division multiplexed pulsed optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed to study the dynamics of a PT symmetry system. Two microwave pulses are used to realize the PT symmetry in a single spatial resonator based on the temporal degrees of freedom. The gain and loss of the microwave pulses and the coupling coefficient between them can then be controlled. We first demonstrate the phase diagram from PT broken to PT symmetry in the OEO system. We theoretically prove that the perturbation of a coupling-induced phase shift larger than causes the disappearance of the PT symmetry. In this experiment, the perturbation is less than ; thus, the phase transition of PT symmetry is observed. In addition, multipairs of PT-symmetry pulses indicate that pulsed OEO could be used to implement complex non-Hermitian Hamilton systems. Therefore, it is confirmed that pulsed OEO is an excellent platform to explore the dynamics of PT symmetry and other non-Hermitian Hamiltonian systems.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(8): 1915

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
2 School of Electronic, Electrical and Communication Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
4 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
5 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518052, China
6 e-mail: ytdai@bupt.edu.cn
Dissipative solitons relying on the double balance between nonlinear and linear effects as well as cavity loss and gain have attracted increasing attention in recent years, since they give rise to novel operating states of various dissipative nonlinear systems. An optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is a dissipative nonlinear microwave photonic system with a high quality factor that has been widely investigated for generating ultra-low noise single-frequency microwave signals. Here, we report a novel operating state of an OEO related to dissipative solitons, i.e., spontaneous frequency hopping related to the formation of dissipative microwave photonic solitons. In this operating state, dissipative microwave photonic solitons occur due to the double balance between nonlinear gain saturation and linear filtering as well as cavity loss and gain in the OEO cavity, creating spontaneous frequency-hopping microwave signals. The generation of wideband tunable frequency-hopping microwave signals with a fast frequency-hopping speed up to tens of nanoseconds is observed in the experiment, together with the corresponding soliton sequences. This work reveals a novel mechanism between the interaction of nonlinear and linear effects in an OEO cavity, extends the suitability and potential applications of solitons, and paves the way for a new class of soliton microwave photonic systems for the generation, processing, and control of microwave and RF signals.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(5): 05001280
1 湖南南华爱斯普林生物技术有限公司, 长沙 410000
2 湖南师范大学医学院医学检验系, 长沙 410013
干细胞治疗作为某些难治性疾病的新型治疗手段, 在组织修复、自身免疫疾病和退行性疾病治疗中具有重要的临床价值。本研究以裸鼠为动物模型, 通过裸鼠皮下成瘤、克隆形成和端粒酶活性等试验, 评估人脐带间充质干细胞的安全性, 为干细胞用于临床治疗的安全性提供参考。裸鼠成瘤性试验结果显示, 阴性对照组和试验组成瘤数均为0, 阳性对照组成瘤数为12。克隆形成试验结果显示, 阴性对照组和试验组无克隆形成, 阳性对照组有克隆形成。端粒酶活性测定结果显示, 阴性对照组端粒酶相对活性为0.01, 阳性对照组端粒酶相对活性为4.33, 试验组 P6代细胞端粒酶相对活性为1.70。因此, 本研究的评估结果显示, 人脐带间充质干细胞在裸鼠中不致瘤, 克隆形成试验结果为阴性, 端粒酶活性测定结果正常, 具有良好的遗传稳定性。人脐带间充质干细胞在本试验中展现了良好的安全性, 具有较好的临床应用价值。
脐带间充质干细胞 端粒 裸鼠成瘤性 克隆形成试验 安全性 umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells telomere tumorigenicity in nude mice clone formation experiment safety
1 南京师范大学物理科学与技术学院, 江苏省光电技术重点实验室, 江苏 南京 210023
2 南京理工大学电子工程与光电技术学院, 江苏 南京 210094
数字全息显微成像技术因能高精度实现定量相位成像的优势受到生物成像与材料科学领域的关注,但共轭像的存在、相位包裹的困扰以及分辨率受限等问题一直阻碍了数字全息显微术的广泛应用。近些年,深度学习作为机器学习中一种对数据特征提取进行特化的模型,在光学成像领域中被广泛应用。除用于提高成像效率外,其解决成像逆问题的潜力也不断被研究人员发掘,为成像领域开辟了一条蹊径。本文从深度学习应用于数字全息显微成像的工作原理出发,介绍它解决光学成像逆问题的思路与重要数理概念,同时对深度学习的完整实施过程进行归纳。扼要地总结了近年来深度学习对于全息重建、自动聚焦与相位恢复、全息去噪与超分辨等方面的研究进展,并对该研究领域中存在的问题与发展趋势进行展望。
成像系统 数字全息显微 深度学习 定量相位成像 激光与光电子学进展
2021, 58(18): 1811006
电子科技大学 电子工程学院,四川 成都 611731
针对宽带高效率功放的设计要求,基于宽带匹配网络设计了一款GaN宽带高效率功率放大器,其工作频率覆盖整个S波段。仿真结果显示,该功放在整个S频段内漏极效率(DE)大于62%,功率附加效率(PAE)大于57%,增益大于10.6 dB。实测结果表明,该功放在整个频段内DE大于54%,PAE大于48%,增益大于9 dB,增益平坦度在1 dB以内,实现了S波段高效率宽带功率放大器的设计。
功率放大器 宽带匹配网络 氮化镓 高效率 power amplifier broadband matching network GaN high efficiency 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报
2018, 16(5): 871
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Lehrstuhl für Medizinphysik, Fakultät für Physik, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Am Coulombwall 1, D-85748, Garching, Germany
2 Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik, D-85748 Garching, Germany
3 Peking University, Beijing 100871, PR China
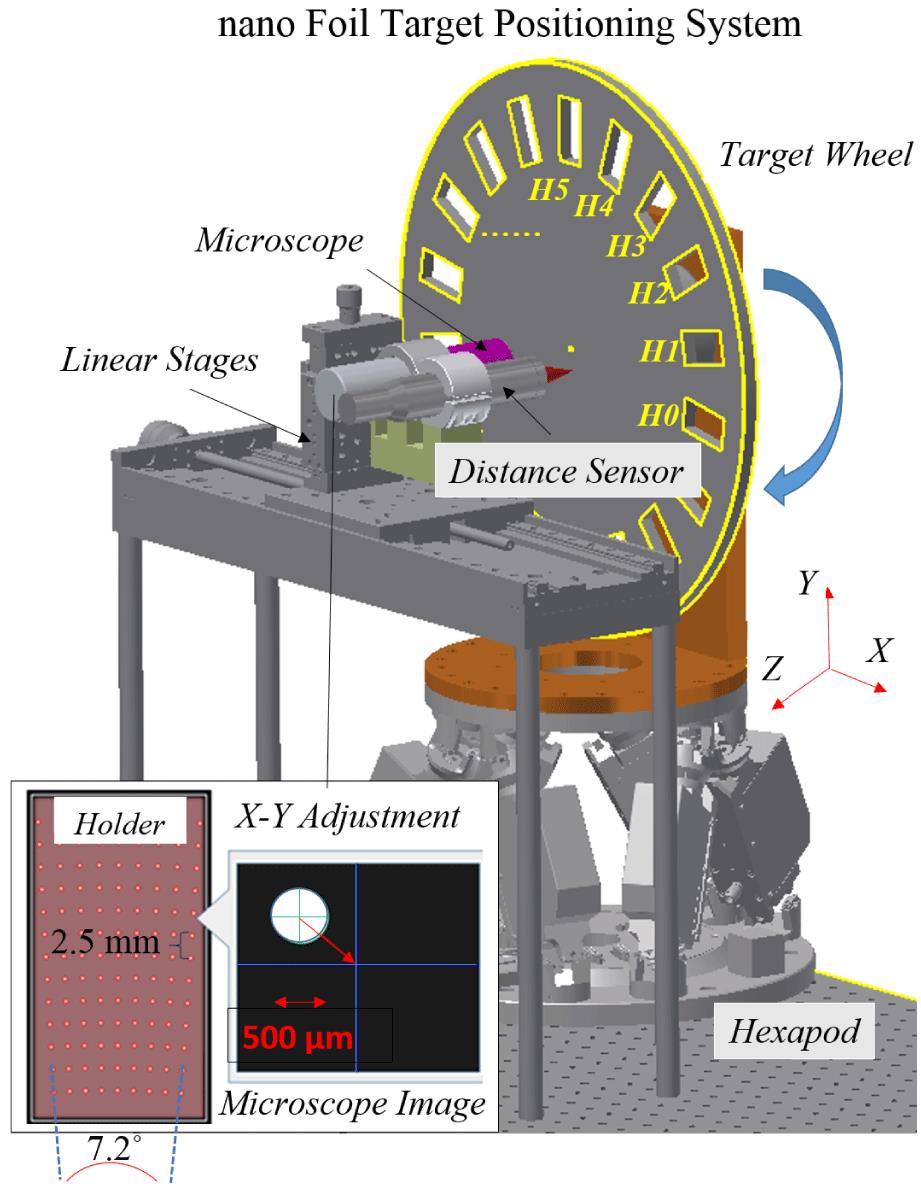
We report on a target system supporting automated positioning of nano-targets with a precision resolution of $4~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ in three dimensions. It relies on a confocal distance sensor and a microscope. The system has been commissioned to position nanometer targets with 1 Hz repetition rate. Integrating our prototype into the table-top ATLAS 300 TW-laser system at the Laboratory for Extreme Photonics in Garching, we demonstrate the operation of a 0.5 Hz laser-driven proton source with a shot-to-shot variation of the maximum energy about 27% for a level of confidence of 0.95. The reason of laser shooting experiments operated at 0.5 Hz rather than 1 Hz is because the synchronization between the nano-foil target positioning system and the laser trigger needs to improve.
high intense laser nm thick target positioning system repetition rated laser-driven ion source High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2017, 5(2): 02000e12
1 江苏大学机械工程学院, 江苏 镇江 212013
2 常州信息职业技术学院, 江苏 常州 213164
将磁场引入激光焊接系统中, 开展了DC51D+AZ镀锌钢和6061铝合金的激光对接焊试验和焊接试样的拉伸试验, 研究了交变磁场对焊缝成形、气孔缺陷、断口形貌、金属间化合物与焊缝力学性能的影响。结果表明, 添加磁场后,焊缝抗拉强度得到提高; 磁场搅拌能改善焊缝的形貌, 减少焊缝中气孔的数量, 细化针状FeAl3相, 抑制脆性Fe/Al化合物的生长, 从而有效提高焊缝的力学性能。
激光技术 磁场搅拌 钢/铝异种金属 激光焊接 金属间化合物
1 北京航空航天大学 仪器科学与光电工程学院,北京 100191
2 第二炮兵装备研究院,北京 100085
高光谱图像具有光谱分辨率高、波段连续、数据量大、图谱合一等特点。然而较高的光谱分辨率会造成波段间相关性强,信息冗余多。所以如何从数百个高光谱波段中选出有利于识别或分类的波段组合成为了高光谱应用需要解决的问题。文章针对相邻波段间相关性较大的特点,提出一种改进的对波段相关矩阵进行全局搜索的子空间划分的波段选择方法。该方法克服了传统只利用相关向量对波段进行划分的缺陷,利用整个相关矩阵进行全局搜索划分,再在划分后的子空间内进行波段选择,从而降低了波段之间的相关性。文章最后使用上述方法对AVIRIS数据进行波段选择,并通过SVM方法对其进行地物分类,结果表明该方法较不进行子空间划分的波段选择方法有较高的分类精度。
波段选择 高光谱图像 子空间划分 band selection hyperspectral image subspace partition 红外与激光工程
2015, 44(10): 3155





